What switch security configuration requires AAA to be configured on the switch?
A. VACL
B. 802.1x
C. Private VLAN
D. port security
What switch security configuration requires AAA to be configured on the switch?
A. VACL
B. 802.1x
C. Private VLAN
D. port security
You have been asked to examine the following output to identify any security problems with the router. Its configuration is shown:
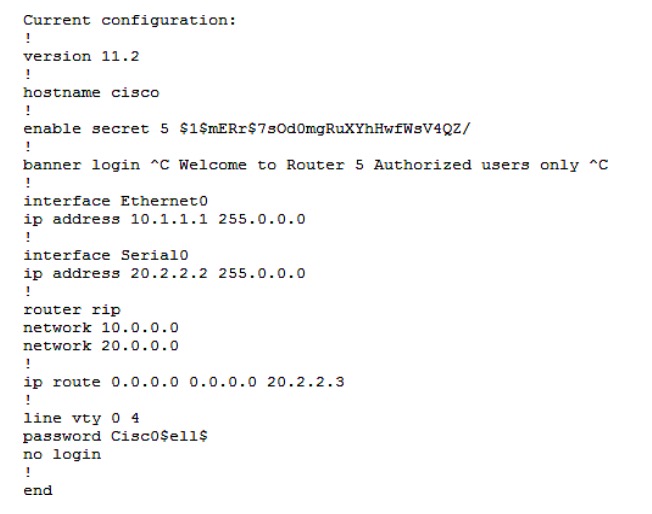
What problems exist? (Choose all that apply.)
A. unencrypted privileged mode password
B. inappropriate wording in the banner message
C. weak password on the VTY line
D. Telnet users will not be prompted for a password
What will be the effect of executing the following command on port F0/1?
switch(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address 00C0.35F0.8301
A. The command statically defines the MAC address of 00c0.35F0.8301 as an allowed host on the switch port.
B. The command expressly prohibits the MAC address of 00c0.35F0.8301 as an allowed host on the switch port.
C. The command configures an inbound access control list on port F0/1 limiting traffic to the IP address of the host.
D. The command encrypts all traffic on the port from the MAC address of 00c0.35F0.8301.
What command disables 802.1x authentication on a port and permits traffic without authentication?
A. dot1x port-control disable
B. dot1x port-control force-unauthorized
C. dot1x port-control auto
D. dot1x port-control force-authorized
Which of the following technologies should be used to prevent a switching loop if a switch is connected to a port configured for PortFast?
A. RSTP
B. BPDU Guard
C. Root Guard
D. PVST
Which of the following cables would be used to connect a router to a switch?
A. v.35
B. crossover
C. rollover
D. straight-through
You are implementing IP SLA and would like to use it to measure hop-by-hop response time between a Cisco router and any IP device on the network.
Which of the following IP SLA operations would you use for this?
A. ICMP path echo operation
B. Internet Control Message Protocol Echo Operation
C. UDP Jitter Operation for VoIP
D. UDP Jitter Operation
Which metric does the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol use for optimal path calculation?
A. MTU
B. Cost
C. Delay
D. Hop count
Which commands would be used to enable Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) on a router, and configure the IP addresses 10.2.2.2 and 192.168.1.1 as a part of complete EIGRP configuration? (Choose three.)
A. router eigrp 10
B. router eigrp
C. network 10.2.2.2
D. network 10.0.0.0
E. network 192.168.1.0
F. network 192.168.1.1
Which Cisco IOS command will display the following partial output?

A. show ip
B. show ip route
C. show ip route summary
D. show route summary