The network administrator has been asked to give reasons for moving from IPv4 to IPv6. What are two valid reasons for adopting IPv6 over IPv4? (Choose two.)
A. no broadcast
B. change of source address in the IPv6 header
C. change of destination address in the IPv6 header
D. Telnet access does not require a password
E. autoconfiguration
F. NAT
CISCO CCNA Exam – Q142
An administrator must assign static IP addresses to the servers in a network. For network 192.168.20.24/29, the router is assigned the first usable host address while the sales server is given the last usable host address. Which of the following should be entered into the IP properties box for the sales server?
A.
IP address: 192.168.20.14
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248
Default Gateway: 192.168.20.9
B.
IP address: 192.168.20.254
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway: 192.168.20.1
C.
IP address: 192.168.20.30
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248
Default Gateway: 192.168.20.25
D.
IP address: 192.168.20.30
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240
Default Gateway: 192.168.20.17
E.
IP address: 192.168.20.30
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240
Default Gateway: 192.168.20.25
CISCO CCNA Exam – Q141
Which subnet mask would be appropriate for a network address range to be subnetted for up to eight LANs, with each LAN containing 5 to 26 hosts?
A. 0.0.0.240
B. 255.255.255.252
C. 255.255.255.0
D. 255.255.255.224
E. 255.255.255.240
CISCO CCNA Exam – Q140
How many bits are contained in each field of an IPv6 address?
A. 24
B. 4
C. 8
D. 16
CISCO CCNA Exam – Q139
What are three approaches that are used when migrating from an IPv4 addressing scheme to an IPv6 scheme. (Choose three.)
A. enable dual-stack routing
B. configure IPv6 directly
C. configure IPv4 tunnels between IPv6 islands
D. use proxying and translation to translate IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets
E. statically map IPv4 addresses to IPv6 addresses
F. use DHCPv6 to map IPv4 addresses to IPv6 addresses
CISCO CCNA Exam – Q138
Refer to the exhibit.
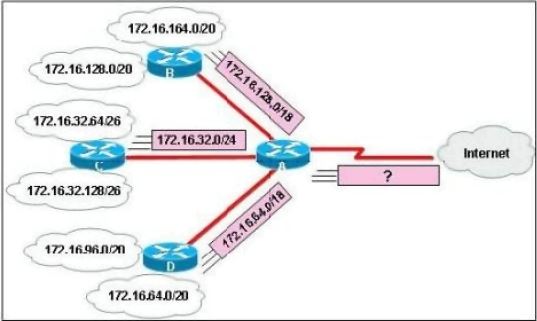
In this VLSM addressing scheme, what summary address would be sent from router A?
A. 172.16.0.0 /16
B. 172.16.0.0 /20
C. 172.16.0.0 /24
D. 172.32.0.0 /16
E. 172.32.0.0 /17
F. 172.64.0.0 /16
CISCO CCNA Exam – Q137
How is an EUI-64 format interface ID created from a 48-bit MAC address?
A. by appending 0xFF to the MAC address
B. by prefixing the MAC address with 0xFFEE
C. by prefixing the MAC address with 0xFF and appending 0xFF to it
D. by inserting 0xFFFE between the upper three bytes and the lower three bytes of the MAC address
E. by prefixing the MAC address with 0xF and inserting 0xF after each of its first three bytes
CISCO CCNA Exam – Q136
Refer to the exhibit.
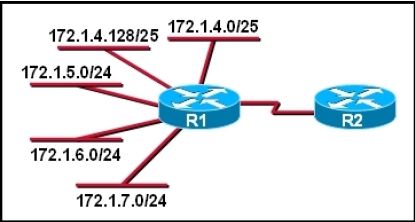
What is the most efficient summarization that R1 can use to advertise its networks to R2?
A.
172.1.0.0/22
B.
172.1.0.0/21
C.
172.1.4.0/22
D.
172.1.4.0/24
172.1.5.0/24
172.1.6.0/24
172.1.7.0/24
E.
172.1.4.0/25
172.1.4.128/25
172.1.5.0/24
172.1.6.0/24
172.1.7.0/24
CISCO CCNA Exam – Q135
Which option is a valid IPv6 address?
A. 2001:0000:130F::099a::12a
B. 2002:7654:A1AD:61:81AF:CCC1
C. FEC0:ABCD:WXYZ:0067::2A4
D. 2004:1:25A4:886F::1
CISCO CCNA Exam – Q134
Which three are characteristics of an IPv6 anycast address? (Choose three.)
A. one-to-many communication model
B. one-to-nearest communication model
C. any-to-many communication model
D. a unique IPv6 address for each device in the group
E. the same address for multiple devices in the group
F. delivery of packets to the group interface that is closest to the sending device