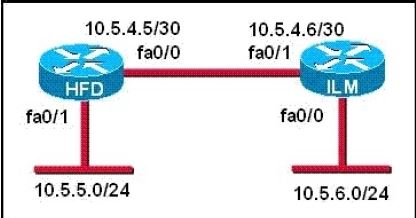
Refer to the exhibit.
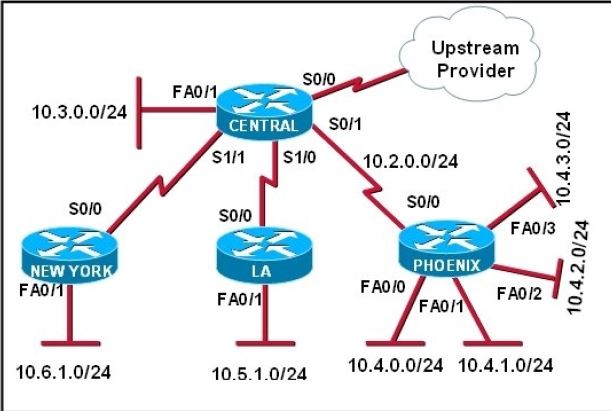
The Lakeside Company has the internetwork in the exhibit. The administrator would like to reduce the size of the routing table on the Central router. Which partial routing table entry in the Central router represents a route summary that represents the LANs in Phoenix but no additional subnets?
A.
10.0.0.0/22 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 10.0.0.0 [90/20514560] via 10.2.0.2, 6w0d, Serial0/1
B.
10.0.0.0/28 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 10.2.0.0 [90/20514560] via 10.2.0.2, 6w0d, Serial0/1
C.
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 10.2.2.0 [90/20514560] via 10.2.0.2, 6w0d, Serial0/1
D.
10.0.0.0/22 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 10.4.0.0 [90/20514560] via 10.2.0.2, 6w0d, Serial0/1
E.
10.0.0.0/28 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 10.4.4.0 [90/20514560] via 10.2.0.2, 6w0d, Serial0/1
F.
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 10.4.4.4 [90/20514560] via 10.2.0.2, 6w0d, Serial0/1