When configuring IPv6 on an interface, which two IPv6 multicast groups are joined? (Choose two)
A. 2000::/3
B. 2002::/5
C. FC00::/7
D. FF02::1
E. FF02::2
When configuring IPv6 on an interface, which two IPv6 multicast groups are joined? (Choose two)
A. 2000::/3
B. 2002::/5
C. FC00::/7
D. FF02::1
E. FF02::2
An engineer is asked to protect unused ports that are configured in the default VLAN on a switch. Which two steps will fulfill the request? (Choose two)
A. Configure the ports in an EtherChannel.
B. Administratively shut down the ports
C. Configure the port type as access and place in VLAN 99
D. Configure the ports as trunk ports
E. Enable the Cisco Discovery Protocol
When configuring a WLAN with WPA2-PSK in the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller GUI, which two formats are available to select? (Choose two)
A. ASCII
B. base64
C. binary
D. decimal
E. hexadecimal
An email user has been lured into clicking a link in an email sent by their company’s security organization. The webpage that opens reports that it was safe but the link could have contained malicious code. Which type of security program is in place?
A. Physical access control
B. Social engineering attack
C. brute force attack
D. user awareness
What is the primary effect of the spanning-tree portfast command?
A. It enables BPDU messages
B. It minimizes spanning-tree convergence time
C. It immediately puts the port into the forwarding state when the switch is reloaded
D. It immediately enables the port in the listening state
In which way does a spine-and-leaf architecture allow for scalability in a network when additional access ports are required?
A. A spine switch and a leaf switch can be added with redundant connections between them
B. A spine switch can be added with at least 40 GB uplinks
C. A leaf switch can be added with a single connection to a core spine switch.
D. A leaf switch can be added with connections to every spine switch
Which output displays a JSON data representation?

Refer to the exhibit. What is the effect of this configuration?

A. All ARP packets are dropped by the switch
B. Egress traffic is passed only if the destination is a DHCP server.
C. All ingress and egress traffic is dropped because the interface is untrusted
D. The switch discards all ingress ARP traffic with invalid MAC-to-IP address bindings.
Refer to the exhibit. What is the effect of this configuration?

A. The switch port interface trust state becomes untrusted
B. The switch port remains administratively down until the interface is connected to another switch
C. Dynamic ARP inspection is disabled because the ARP ACL is missing
D. The switch port remains down until it is configured to trust or untrust incoming packets
Refer to the exhibit. Which route does R1 select for traffic that is destined to 192 168.16.2?
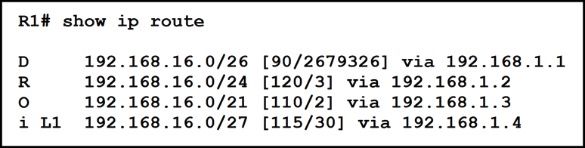
A. 192.168.16.0/21
B. 192.168.16.0/24
C. 192.168 26.0/26
D. 192.168.16.0/27