Which encapsulation type is a Frame Relay encapsulation type that is supported by Cisco routers?
A. IETF
B. ANSI Annex D
C. Q9333-A Annex A
D. HDLC
Which encapsulation type is a Frame Relay encapsulation type that is supported by Cisco routers?
A. IETF
B. ANSI Annex D
C. Q9333-A Annex A
D. HDLC
RouterA is unable to reach RouterB. Both routers are running IOS version 12.0.
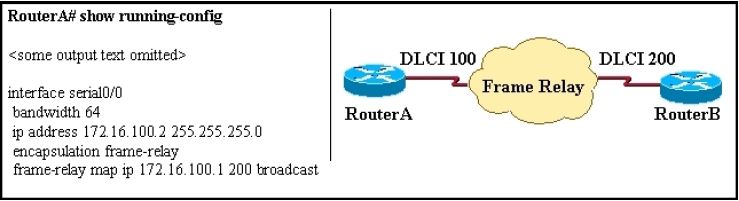
After reviewing the command output and graphic, what is the most likely cause of the problem?
A. incorrect bandwidth configuration
B. incorrect LMI configuration
C. incorrect map statement
D. incorrect IP address
Refer to the exhibit.

What is the meaning of the term dynamic as displayed in the output of the show frame-relay map command shown?
A. The Serial0/0 interface is passing traffic.
B. The DLCI 100 was dynamically allocated by the router.
C. The Serial0/0 interface acquired the IP address of 172.16.3.1 from a DHCP server.
D. The DLCI 100 will be dynamically changed as required to adapt to changes in the Frame Relay cloud.
E. The mapping between DLCI 100 and the end station IP address 172.16.3.1 was learned through Inverse ARP.
Which statement describes the process ID that is used to run OSPF on a router?
A. It is globally significant and is used to represent the AS number.
B. It is locally significant and is used to identify an instance of the OSPF database.
C. It is globally significant and is used to identify OSPF stub areas.
D. It is locally significant and must be the same throughout an area.
Which statement is correct regarding the operation of DHCP?
A. A DHCP client uses a ping to detect address conflicts.
B. A DHCP server uses a gratuitous ARP to detect DHCP clients.
C. A DHCP client uses a gratuitous ARP to detect a DHCP server.
D. If an address conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool and an administrator must resolve the conflict.
E. If an address conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool for an amount of time configurable by the administrator.
F. If an address conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool and will not be reused until the server is rebooted.
Refer to the exhibit.
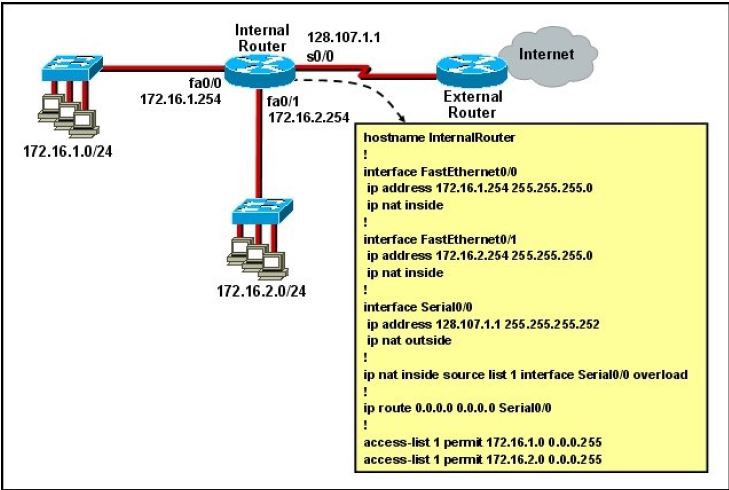
What statement is true of the configuration for this network?
A. The configuration that is shown provides inadequate outside address space for translation of the number of inside addresses that are supported.
B. Because of the addressing on interface FastEthernet0/1, the Serial0/0 interface address will not support the NAT configuration as shown.
C. The number 1 referred to in the ip nat inside source command references access-list number 1.
D. ExternalRouter must be configured with static routes to networks 172.16.1.0/24 and 172.16.2.0/24.
Which statement describes the process of dynamically assigning IP addresses by the DHCP server?
A. Addresses are allocated after a negotiation between the server and the host to determine the length of the agreement.
B. Addresses are permanently assigned so that the hosts uses the same address at all times.
C. Addresses are assigned for a fixed period of time, at the end of the period, a new request for an address must be made.
D. Addresses are leased to hosts, which periodically contact the DHCP server to renew the lease.
What are two benefits of using NAT? (Choose two.)
A. NAT facilitates end-to-end communication when IPsec is enabled.
B. NAT eliminates the need to re-address all hosts that require external access.
C. NAT conserves addresses through host MAC-level multiplexing.
D. Dynamic NAT facilitates connections from the outside of the network.
E. NAT accelerates the routing process because no modifications are made on the packets.
F. NAT protects network security because private networks are not advertised.
On which options are standard access lists based?
A. destination address and wildcard mask
B. destination address and subnet mask
C. source address and subnet mask
D. source address and wildcard mask
A network engineer wants to allow a temporary entry for a remote user with a specific username and password so that the user can access the entire network over the Internet. Which ACL can be used?
A. standard
B. extended
C. dynamic
D. reflexive