How many broadcast domains are shown in the graphic assuming only the default VLAN is configured on the switches?
A. one
B. two
C. six
D. twelve
Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.)
A. 802.1Q native VLAN frames are untagged by default.
B. 802.1Q trunking ports can also be secure ports.
C. 802.1Q trunks can use 10 Mb/s Ethernet interfaces.
D. 802.1Q trunks require full-duplex, point-to-point connectivity.
E. 802.1Q trunks should have native VLANs that are the same at both ends.
Refer to the exhibit.
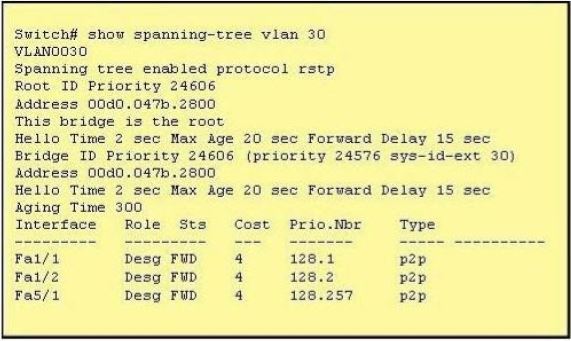
The output that is shown is generated at a switch. Which three statements are true? (Choose three.)
A. All ports will be in a state of discarding, learning, or forwarding.
B. Thirty VLANs have been configured on this switch.
C. The bridge priority is lower than the default value for spanning tree.
D. All interfaces that are shown are on shared media.
E. All designated ports are in a forwarding state.
F. This switch must be the root bridge for all VLANs on this switch.
Which term describes a spanning-tree network that has all switch ports in either the blocking or forwarding state?
A. converged
B. redundant
C. provisioned
D. spanned
What are the possible trunking modes for a switch port? (Choose three.)
A. transparent
B. auto
C. on
D. desirable
E. client
F. forwarding
Which two of these statements regarding RSTP are correct? (Choose two.)
A. RSTP cannot operate with PVST+.
B. RSTP defines new port roles.
C. RSTP defines no new port states.
D. RSTP is a proprietary implementation of IEEE 802.1D STP.
E. RSTP is compatible with the original IEEE 802.1D STP.
Refer to the exhibit.
Which two statements are true of the interfaces on Switch1? (Choose two.)
A. Multiple devices are connected directly to FastEthernet0/1.
B. A hub is connected directly to FastEthernet0/5.
C. FastEthernet0/1 is connected to a host with multiple network interface cards.
D. FastEthernet0/5 has statically assigned MAC addresses.
E. FastEthernet0/1 is configured as a trunk link.
F. Interface FastEthernet0/2 has been disabled.
Three switches are connected to one another via trunk ports. Assuming the default switch configuration, which switch is elected as the root bridge for the spanning-tree instance of VLAN 1?
A. the switch with the highest MAC address
B. the switch with the lowest MAC address
C. the switch with the highest IP address
D. the switch with the lowest IP address
What are three advantages of VLANs? (Choose three.)
A. VLANs establish broadcast domains in switched networks.
B. VLANs utilize packet filtering to enhance network security.
C. VLANs provide a method of conserving IP addresses in large networks.
D. VLANs provide a low-latency internetworking alternative to routed networks.
E. VLANs allow access to network services based on department, not physical location.
F. VLANs can greatly simplify adding, moving, or changing hosts on the network.