Which command can you enter to display the hits counter for NAT traffic?
A. show ip nat statistics
B. debug ip nat
C. show ip debug nat
D. clear ip nat statistics
Which command can you enter to display the hits counter for NAT traffic?
A. show ip nat statistics
B. debug ip nat
C. show ip debug nat
D. clear ip nat statistics
Which standards-based First Hop Redundancy Protocol is a Cisco supported alternative to Hot Standby Router Protocol?
A. VRRP
B. GLBP
C. TFTP
D. DHCP
Refer to the exhibit.
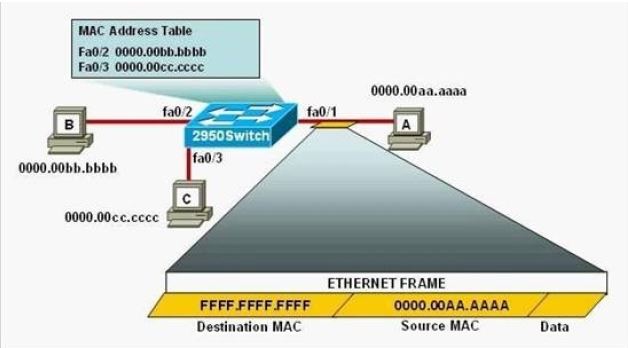
The following commands are executed on interface fa0/1 of 2950Switch.
2950Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security
2950Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
2950Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 1
The Ethernet frame that is shown arrives on interface fa0/1. What two functions will occur when this frame is received by 2950Switch? (Choose two.)
A. The MAC address table will now have an additional entry of fa0/1 FFFF.FFFF.FFFF.
B. Only host A will be allowed to transmit frames on fa0/1.
C. This frame will be discarded when it is received by 2950Switch.
D. All frames arriving on 2950Switch with a destination of 0000.00aa.aaaa will be forwarded out fa0/1.
E. Hosts B and C may forward frames out fa0/1 but frames arriving from other switches will not be forwarded out fa0/1.
F. Only frames from source 0000.00bb.bbbb, the first learned MAC address of 2950Switch, will be forwarded out fa0/1.
What will be the result if the following configuration commands are implemented on a Cisco switch?
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
A. A dynamically learned MAC address is saved in the startup-configuration file.
B. A dynamically learned MAC address is saved in the running-configuration file.
C. A dynamically learned MAC address is saved in the VLAN database.
D. Statically configured MAC addresses are saved in the startup-configuration file if frames from that address are received.
E. Statically configured MAC addresses are saved in the running-configuration file if frames from that address are received.
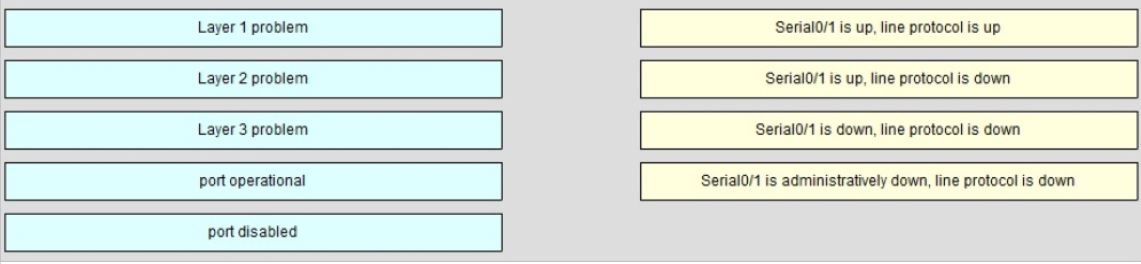
Drag each category on the left to its corresponding router output line on the right. Each router output line is the result of a show ip interface command. Not all categories are used.
Select and Place:
A user is unable to connect to the Internet. Based on the layered approach to troubleshooting and beginning with the lowest layer, drag each procedure on the left to its proper category on the right.
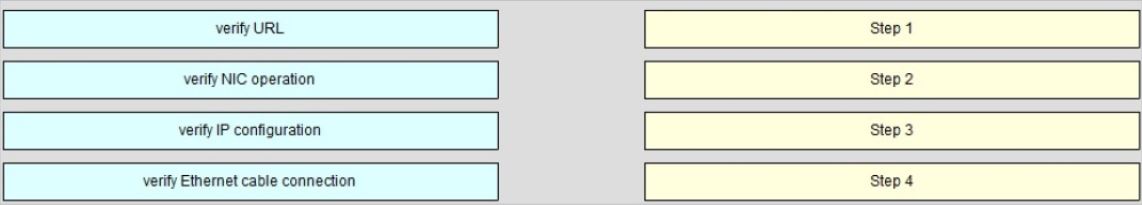
Select and Place:

Refer to the exhibit.
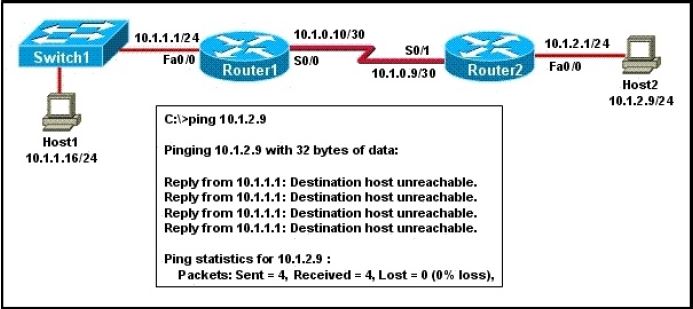
A network administrator attempts to ping Host2 from Host1 and receives the results that are shown. What is the problem?
A. The link between Host1 and Switch1 is down.
B. TCP/IP is not functioning on Host1
C. The link between Router1 and Router2 is down.
D. The default gateway on Host1 is incorrect.
E. Interface Fa0/0 on Router1 is shutdown.
F. The link between Switch1 and Router1 is down.
Refer to the exhibit.
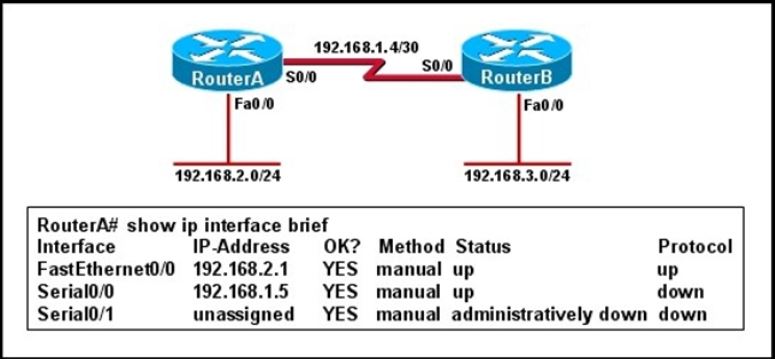
Hosts in network 192.168.2.0 are unable to reach hosts in network 192.168.3.0. Based on the output from RouterA, what are two possible reasons for the failure? (Choose two.)
A. The cable that is connected to S0/0 on RouterA is faulty.
B. Interface S0/0 on RouterB is administratively down.
C. Interface S0/0 on RouterA is configured with an incorrect subnet mask.
D. The IP address that is configured on S0/0 of RouterB is not in the correct subnet.
E. Interface S0/0 on RouterA is not receiving a clock signal from the CSU/DSU.
F. The encapsulation that is configured on S0/0 of RouterB does not match the encapsulation that is configured on S0/0 of RouterA.
Refer to the exhibit.
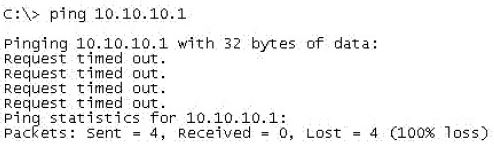
An administrator pings the default gateway at 10.10.10.1 and sees the output as shown. At which OSI layer is the problem?
A. data link layer
B. application layer
C. access layer
D. session layer
E. network layer
Refer to the exhibit.
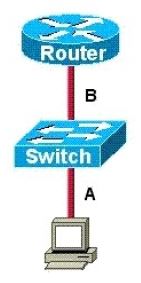
The two connected ports on the switch are not turning orange or green. What would be the most effective steps to troubleshoot this physical layer problem? (Choose three.)
A. Ensure that the Ethernet encapsulations match on the interconnected router and switch ports.
B. Ensure that cables A and B are straight-through cables.
C. Ensure cable A is plugged into a trunk port.
D. Ensure the switch has power.
E. Reboot all of the devices.
F. Reseat all cables.