The topology below is running OSPF. You are required to troubleshoot and resolve the OSPF issues between the various routers. Use the appropriate show commands to troubleshoot the issues.
CCNA – Access List Simulation 2
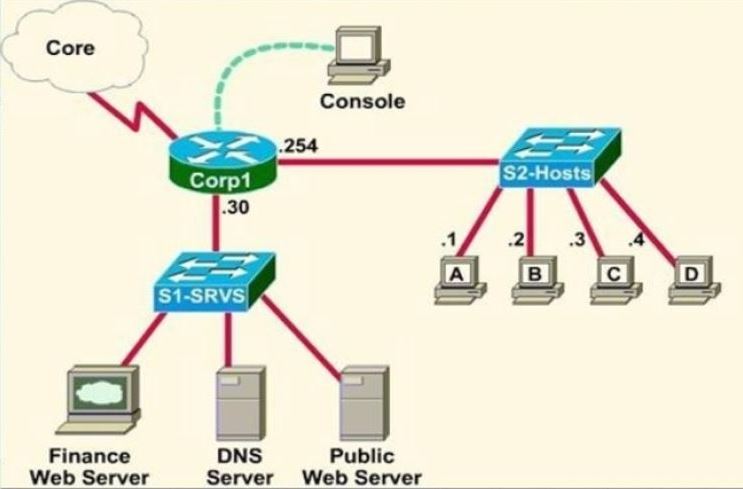
A network associate is adding security to the configuration of the Corp1 router. The user on host C should be able to use a web browser to access financial information from the Finance Web Server. No other hosts from the LAN nor the Core should be able to use a web browser to access this server. Since there are multiple resources for the corporation at this location including other resources on the Finance Web Server, all other traffic should be allowed.
The task is to create and apply an access-list with no more than three statements that will allow ONLY host C web access to the Finance Web Server (172.22.242.23). No other hosts will have web access to the Finance Web Server. All other traffic is permitted.
CCNA – Access List Simulation 1
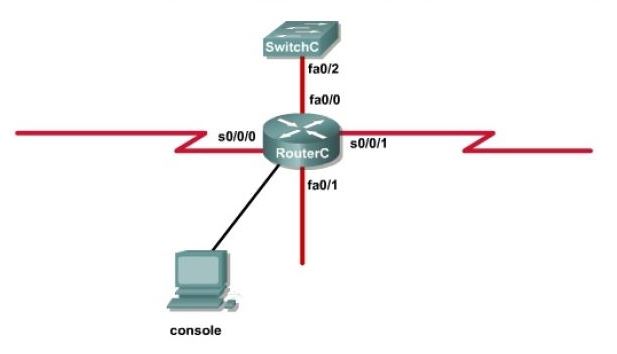
An administrator is trying to ping and telnet from SwitchC to RouterC with the results shown below.

Click the console connected to RouterC and issue the appropriate commands to answer the questions.
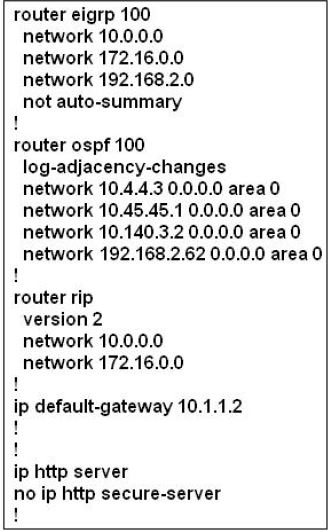
For this question we only need to use the “show running-config” command to answer all the questions below
Router>enable
Router#show running-config

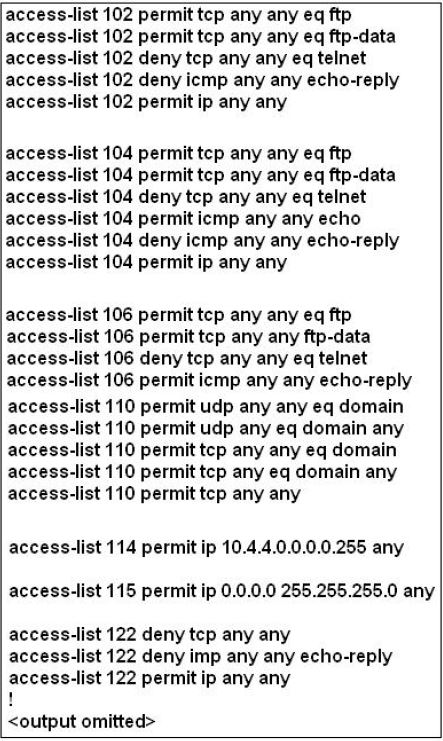
Access List Simulation – Question 1
How can we fix the problem but only allow ping to work while disabling telnet?
A. Correctly assign an IP address to interface fa0/1
B. Change the ip access-group command on fa0/0 from “in” to “out”
C. Remove access-group 106 in from interface fa0/0 and add access-group 115 in.
D. Remove access-group 102 out from interface s0/0/0 and add access-group 114 in
E. Remove access-group 106 in from interface fa0/0 and add access-group 104 in
Access List Simulation – Question 2
What will happen after issuing the command “ip access-group 114 in” to the fa0/0 interface?
A. Attempts to telnet to the router would fail
B. All traffic from the 10.4.4.0 network would be allow to go through
C. TCP and UDP traffic are not allowed to pass
D. Routing protocol updates for the 10.4.4.0 network would not be accepted from the fa0/0 interface
Access List Simulation – Question 3
What will happen after issuing the command “access-group 115 in” on the s0/0/1 interface?
A. Hosts cannot connect to Router through s0/0/1
B. Telnet and ping would work but routing updates would fail.
C. FTP, FTP-DATA, echo, and HTTP traffic would work but telnet would fail
D. Only traffic from the 10.4.4.0 network would pass through the interface
CISCO CCNA Exam – Q335
A network administrator needs to configure a serial link between the main office and a remote location. The router at the remote office is a non-Cisco router. How should the network administrator configure the serial interface of the main office router to make the connection?
A.
Main(config)# interface serial 0/0
Main(config-if)# ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.252
Main(config-if)# no shut
B.
Main(config)# interface serial 0/0
Main(config-if)# ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.252
Main(config-if)# encapsulation ppp
Main(config-if)# no shut
C.
Main(config)# interface serial 0/0
Main(config-if)# ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.252
Main(config-if)# encapsulation frame-relay
Main(config-if)# authentication chap
Main(config-if)# no shut
D.
Main(config)# interface serial 0/0
Main(config-if)#ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.252
Main(config-if)#encapsulation ietf
Main(config-if)# no shut
CISCO CCNA Exam – Q334
What are three reasons that an organization with multiple branch offices and roaming users might implement a Cisco VPN solution instead of point-to-point WAN links? (Choose three.)
A. reduced cost
B. better throughput
C. broadband incompatibility
D. increased security
E. scalability
F. reduced latency
CISCO CCNA Exam – Q333
Which two statistics appear in “show frame-relay map” output? (Choose two.)
A. the number of BECN packets that are received by the router
B. the value of the local DLCI
C. the number of FECN packets that are received by the router
D. the status of the PVC that is configured on the router
E. the IP address of the local router
CISCO CCNA Exam – Q332
Users have been complaining that their Frame Relay connection to the corporate site is very slow. The network administrator suspects that the link is overloaded.
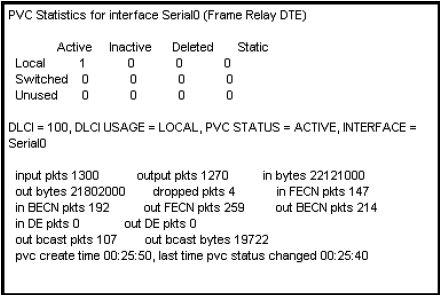
Based on the partial output of the Router# show frame relay pvc command shown in the graphic, which output value indicates to the local router that traffic sent to the corporate site is experiencing congestion?
A. DLCI = 100
B. last time PVC status changed 00:25:40
C. in BECN packets 192
D. in FECN packets 147
E. in DE packets 0
CISCO CCNA Exam – Q331
Which command allows you to verify the encapsulation type (CISCO or IETF) for a Frame Relay link?
A. show frame-relay lmi
B. show frame-relay map
C. show frame-relay pvc
D. show interfaces serial
CISCO CCNA Exam – Q330
It has become necessary to configure an existing serial interface to accept a second Frame Relay virtual circuit. Which of the following procedures are required to accomplish this task? (Choose three.)
A. Remove the IP address from the physical interface.
B. Encapsulate the physical interface with multipoint PPP.
C. Create the virtual interfaces with the interface command.
D. Configure each subinterface with its own IP address.
E. Disable split horizon to prevent routing loops between the subinterface networks.
F. Configure static Frame Relay map entries for each subinterface network.
CISCO CCNA Exam – Q329
What occurs on a Frame Relay network when the CIR is exceeded?
A. All TCP traffic is marked discard eligible.
B. All UDP traffic is marked discard eligible and a BECN is sent.
C. All TCP traffic is marked discard eligible and a BECN is sent.
D. All traffic exceeding the CIR is marked discard eligible.


